Contraception » Vaginal ring
vaginal ring (Nuvaring)
The vaginal ring contains two hormones - oestrogen and progesterone.
How effective is it?
More than 99% effective when used perfectly.
91% effective in real-life.
How does it work?
The main way the vaginal ring works is to stop the ovaries from releasing an egg each month (ovulation).
Where can I get the vaginal ring?
In Dumfries and Galloway you can get the vaginal ring from your GP, the local sexual health services or a C2U drop-in if you are under 20.
Can anyone use the vaginal ring?
Not everyone can use the vaginal ring. Although there are some medical conditions that would mean you should not use the vaginal ring, decisions often depend on a combination of age, smoking, the severity of any medical condition, whether there are other health problems and sometimes your family history of illness. Each woman’s situation is different and your doctor or nurse will be able to advise you.
Conditions which may mean you should not use the vaginal ring.
- You are breast feeding and your baby is less than 6 weeks old
- You are 35 or older and smoke
- You have a history of certain types of migraine
- You develop migraine for the first time whilst using the vaginal ring
- You have had at any time a blood clot in a vein or artery
- You have a close relative who has had a blood clot in a vein under the age of 45
- You have certain types of heart abnormalities, previous stroke, problems with your circulation or high blood pressure
- You have had breast cancer
- You have had certain types of liver or gall bladder disease
- You have had diabetes for a long time or have complications with it
- You are significantly overweight (BMI 35 or above)
- You have antiphospholipid antibodies
- You have prolonged immobility e.g. wheelchair use or after major surgery etc.
Many women who cannot use the vaginal ring are often able to use contraception which only contains the hormone progesterone. This can be taken as the progesterone only pill, implant, injection or hormone coil. There is also contraception that doesn’t contain any hormones such as a copper coil, condoms and diaphragms.
How old do I have to be to use the vaginal ring?
Once your periods have started you can use the vaginal ring.
Can I only use the vaginal ring for a certain length of time or have to stop at a certain age?
If you are well on the vaginal ring and nothing changes in your own or family medical history then there would be reason to stop the vaginal ring. In fact if you are healthy, do not smoke and there are no medical reasons for you not to use the vaginal ring you could use it until the age of 50.
What are the advantages of the vaginal ring?
Some of the good things about the vaginal ring are:
- Usually makes your periods regular, lighter and less painful
- May help with premenstrual tension
- Reduces the risk of cancer of the womb, ovary and bowel
What are the disadvantages of the vaginal ring?
- When you start the vaginal ring you may get headaches, nausea, breast tenderness, mood changes and some bleeding when you don‘t expect it. These normally stop within the first few months but if you are concerned or these symptoms continue then talk to a nurse or doctor about it.
- The ring may increase your blood pressure and this will be measured regularly.
- The ring does not protect you against sexually transmitted infections and many women choose to use condoms as well.
The vaginal ring can have some serious side effects which are not common.
These include:
- A very small number of women may develop a blood clot which can block a vein (causing a venous thrombosis). or an artery (causing an arterial thrombosis), heart attack or stroke
- There may be a small increase in the risk of breast cancer in women who have used the vaginal ring but remember the vaginal ring does reduce the chance of cancer of the ovary and the womb.
The risk of a venous thrombosis is greatest during the first year that you use the vaginal ring and if any of the following apply to you: you are very overweight, are immobile for a long period of time or use a wheelchair, have severe varicose veins or a member of your immediate family had a venous thrombosis before they were 45
Arterial thrombosis
The risk of arterial thrombosis is greater if you smoke, are diabetic, have high blood pressure, are very overweight, have certain sorts of migraines or a member of your immediate family had a heart attack or stroke before they were 45.
You should see a doctor straight away if you develop any of the following symptoms:
- Pain in the chest, including any sharp pain which is worse when you breathe in
- Breathlessness
- Coughing up blood
- Weakness, numbness, or bad 'pins and needles' of an arm or leg
- Severe stomach pain
- A bad fainting attack or a collapse
- Unusual headaches or migraines that are worse than usual
- Sudden problems with speech or eyesight
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice)
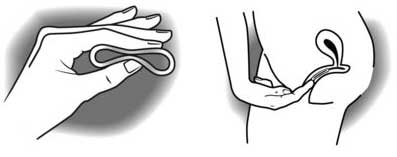
How do I insert the vaginal ring?
Your doctor or nurse should advise you on how to insert and remove the vaginal ring. With clean hands squeeze the ring between your thumb and finger and use one hand to insert it into your vagina. If necessary, spread your labia (vaginal lips) with your other hand. Push the ring into your vagina until it feels comfortable. It does not need to cover your cervix (entrance to the uterus) to work.
How will I know the vaginal ring is in place?
The ring does not need to be in an exact position. Most women can’t feel the ring. If you can feel it and it is also uncomfortable, push the ring a little further into your vagina. You can check it’s still there with your fingers.
There is no danger that the vaginal ring can get lost inside the vagina – it is stopped by the cervix. However, if you are sure it’s inside you but you can’t feel it with your fingers, see a doctor or nurse.
Will I, or my partner, be able to feel the vaginal ring during sex?
Occasionally, you or your partner might be able to feel the ring during sex. This is not uncomfortable or unpleasant for most people. The ring is not likely to affect or harm your partner.
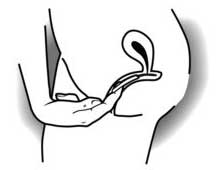
How do I remove the vaginal ring?
Remove the vaginal ring by hooking a finger under it, or by grasping it between your thumb and finger, and gently pulling it out.
If you experience pain or bleeding when trying to remove the ring, or cannot remove it, tell your doctor or nurse immediately.
How to use the ring?
There are different ways of using the vaginal ring. The ring is designed to give you a withdrawal bleed once a month. A withdrawal bleed isn’t the same as your period. It’s caused by you not getting hormones on a ring-free break. Ring instructions tell you to take a seven day ring-free break but you can choose to shorten this break or to miss it and not have a withdrawal bleed.
Missing or shortening the ring-free break could help you if you get heavy or painful bleeding, headaches or mood swings on ring-free days. The riskiest time to forget your ring is just before or just after the ring-free break. You’re more at risk of pregnancy so taking a shorter break or missing a break makes this less risky.
You can use the ring in the following ways.
- Leave the vaginal ring in for 21 days then remove it and wait for 4 or 7 days. This has been the standard way to use the ring. You’ll usually have a withdrawal bleed during the ring-free break. This is called a ring cycle. Start using the ring again on the fifth or eighth day, even if you’re still bleeding.
- Leave the vaginal ring in for 21 days then remove it and insert a new one immediately. Leave that in for another 21 days. Remove it and insert a new one immediately. Leave that in for another 21 days. Take a break for 4 or 7 days before inserting a new one. This is called extended use or tricycling. You’ll usually have a withdrawal bleed during the ring-free break. Start using the ring again on the fifth or eighth day even if you’re still bleeding.
- Leave the vaginal ring in for 21 days. Remove it and insert a new one immediately. Continue to remove and insert a new ring after 21 days with no breaks. This is called continuous use. You don’t have a withdrawal bleed but you may still get some bleeding which may be occasional or more frequent. Any bleeding you get is likely to reduce over time if you keep using the ring continuously.
- Leave the vaginal ring in for at least 21 days. Remove it and insert a new one immediately. Continue to remove and insert a new ring after 21 days. If you get bleeding that’s unacceptable to you for 3-4 days then remove the ring for a four day ring-free break. This is called flexible extended use. Insert a new ring again on the fifth day even if you’re still bleeding. This can help manage the bleeding. Leave the ring in for at least 21 days before taking your next break.
You can use the ring continuously without a break for as long as you like, as long as your doctor or nurse doesn’t advise you to stop.
Disposing of the vaginal ring:
Put the used vaginal ring in the disposal sachet provided and place it in a waste bin. It must not be flushed down the toilet.
Am I protected from pregnancy during the seven day, ring-free interval?
Yes. You are protected if:
- you used the vaginal ring according to instructions during the last three weeks and
- you start the next ring cycle on time and
- you are not taking medicines that will affect the ring (see If I take medicines will it affect the vaginal ring?).
What if I forget to take the vaginal ring out at the end of week three?
Seven days or less
Up to seven days.
If the ring has been left in for up to seven days after the end of week three (up to four weeks in total):
- As soon as you remember, remove the ring. Do not put another ring in. Start your seven day, ringfree interval. After the seven days insert a new ring on the same day of the week you removed it.
- You don’t need to use additional contraception and you are protected against pregnancy.
More than seven days
If the ring has been left in for more than seven days after the end of week three (more than four weeks in total):
- As soon as you remember, remove the ring and insert a new ring immediately.
- You must use additional contraception until the new ring has been in place for seven continuous days.
- Ask your doctor or nurse for advice if you have had sex in the previous few days and were not using a condom as you may need emergency contraception.
What if I forget to put a new vaginal ring in at the end of the ring-free interval?
Insert a new ring as soon as you remember and use additional contraception until a new ring has been in place for seven continuous days. Ask your doctor or nurse for advice if you have had sex in the previous few days and were not using a condom as you may need emergency contraception.
What should I do if the ring comes out of my vagina for a short time?
The longer the ring has been out of the vagina, the higher the risk of pregnancy. You may also experience breakthrough bleeding.
If the ring comes out of the vagina for:
Less than 48 hours:
- Insert the ring as soon as possible.
- Keep the ring in until the next scheduled ring-free break.
- If you’re in the first week after a ring-free break, you don’t need to use any additional contraception as long you’ve used the ring correctly every other day this week and in the seven days before the ring-free break.
- If you’re in any other week, you don’t need to use any additional contraception as long you’ve used the ring correctly for the previous seven days.
More than 48 hours:
- Insert the ring as soon as possible.
- Keep the ring in until the next scheduled ring-free break.
- You may need emergency contraception now and a pregnancy test in three weeks if you’re in the first week after a ring-free break and had unprotected sex this week or during the ring-free break. Use condoms or avoid sex until the ring has been in place for seven days in a row.
- You don’t need emergency contraception if you’re in any other week and the ring has been used correctly in the previous seven days. Use condoms or avoid sex until the ring has been in place for seven days in a row and if you’re within seven days of a ring-free break, omit it.
Can the ring fall out of my vagina?
The muscles of your vagina hold the ring in place. Occasionally, however, the ring may come out of your vagina (expulsion), for example if it wasn’t inserted properly, during sex or a bowel movement (having a poo), or while removing a tampon. If this happens often, you may want to consider another method of contraception.
Research shows that the ring is not more likely to come out if you have had children.
What if the ring breaks inside my vagina?
This is very rare and it is unlikely to affect how the ring works. It will not harm you. Remove the broken ring and insert a new one as soon as possible. Continue with the cycle that you were on.
If I take medicines will it affect the vaginal ring?
There are a few medicines that make the vaginal ring less effective. You should tell a doctor or nurse that you are using the vaginal ring if you are prescribed any new medication so that they can check to see if there are any interactions.
Commonly prescribed antibiotics do not affect the vaginal ring. However some drugs can reduce the effectiveness of the vaginal ring and increase the chance of getting pregnant. These include certain drugs used to treat HIV, TB and epilepsy as well as the herbal preparation St. John’s Wort. If you are taking any of these tablets you should speak to your doctor about the contraceptive options available to you. Ella-One should be avoided if you are on hormonal contraception and if you are given Ella-One because you haven’t used your ring for a few days, you should not restart your ring for another 5 days. It will then take a further 7 days until you have effective contraception so you should abstain or use condoms for this timeTreatments for thrush do not affect the effectiveness of the ring.
Finally
It is important that you are happy with the type of contraception you choose to use. Doctors and nurses are trained to work with you to find a method of contraception that suits you. Do not be afraid to discuss any concerns you may have.
